With the advancements in Industrial Edge and Cloud computing technologies, manufacturers now have access to scalable and flexible computing resources. These resources are instrumental in storing, analyzing, and visualizing massive amounts of data that industrial systems generate. They also play a crucial role in addressing the growing concern of cybersecurity threats.
Key technologies for Industrial Edge and Cloud architectures
One of the key technology trends in Industrial Edge and Cloud architectures is MQTT. This messaging protocol facilitates real-time communication between edge devices, such as sensors and cloud-based applications. To streamline data traffic, companies are deploying an MQTT broker at the edge level. Acting as a central hub, this broker ensures that data is efficiently streamed towards the central platform. Moreover, local applications can be accessed through the MQTT broker.
Using MQTT, devices and applications can seamlessly exchange data. There are various protocols available for connecting applications to the Internet or the Cloud. However, MQTT has emerged as the preferred protocol for transmitting data over an Internet connection in most industrial applications. Unlike the traditional method of continuously checking devices for data changes, MQTT allows applications to “report by exception,” meaning that data is only written when changes occur.
KPA Automation softPLC supports MQTT and allows devices to subscribe and publish data to specific devices, enabling tailored data interaction. With MQTT, a device can be configured to subscribe only to the essential data, avoiding unnecessary information overload. Security is a crucial aspect of any industrial application, and MQTT excels in this area as well. It provides encrypted and authenticated access to your data, making it a perfect fit for IIoT applications.
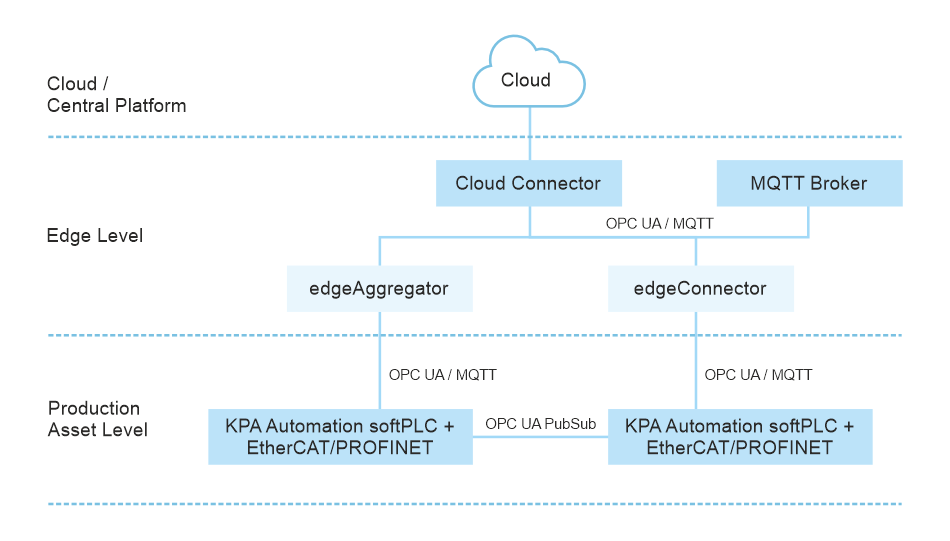
The Industrial Edge and Cloud computing technologies have revolutionized smart manufacturing by providing essential computing resources and addressing security challenges. With MQTT as a fundamental part of these architectures, manufacturers can enhance their operations by enabling seamless communication between edge devices and Cloud applications.
Another key technology that Industrial Edge architectures utilize is edge computing. Edge computing devices come equipped with integrated cybersecurity features to process, analyze, and manage data at the network’s edge. In the manufacturing context, edge computing refers to a decentralized system of edge nodes positioned in close proximity to physical data sources. These edge nodes are connected to both devices and a central platform, such as a Cloud. Unlike components at the production asset level, edge nodes can be centrally managed, with data processing occurring either within the node itself or by the central platform. By performing local processing, data quality is improved, and the amount of data transmitted to the Cloud is reduced, resulting in faster response times and enhanced connectivity.
Moreover, Cloud applications provide scalable and flexible computing resources for storing, analyzing, and visualizing the substantial volumes of data generated by industrial systems. These applications offer advanced analytics, machine learning capabilities, predictive maintenance functionalities, remote monitoring and supervisory control HMIs, and much more.
Industrial Edge benefits for manufacturers
Manufacturers can derive numerous advantages from leveraging Industrial Edge and Cloud computing, including enhanced cybersecurity, data democratization, scalability, and simplified management of industrial systems.
Enhanced Cybersecurity
Industrial Edge and Cloud architectures incorporate secure communication protocols, data encryption, access control, and authentication mechanisms to safeguard industrial infrastructure, data, and operations from unauthorized access and data breaches. It is crucial to deploy these cybersecurity measures at both the edge and cloud layers. In industrial settings, cybersecurity assumes paramount importance. Communication technologies such as MQTT and TLS (transport layer security) address cybersecurity concerns within industrial edge-to-cloud architectures by originating from the edge. Secure communications originate from the edge device without the need for open inbound firewall ports for data transportation. Edge devices solely publish their data outbound, and software applications subscribe to this data using equally secure methods.
Data democratization
By centralizing data storage and analysis in the Cloud, authorized personnel can retrieve real-time and historical data from any location. This accessibility improves decision-making, enhances performance optimization, and streamlines operations. The key to democratizing operational data lies in reducing the dependence between data-generating devices and the software applications that require the data. MQTT facilitates this decoupled architecture by brokering all data messages through a server. Multiple publishers can send their data to the broker, while multiple subscribers can select the data they need from the published content. This enables all stakeholders to work with the data simultaneously.
Scalability
The amount of data we generate is continually increasing, and our operational needs are expanding. However, both Industrial Edge and Cloud architectures have the capability to easily adapt to these growing demands. Cloud computing offers access to virtually limitless storage and computing resources. On the other hand, edge computing allows us to distribute data processing to effectively handle the ever-growing workloads.
Easier way to manage industrial systems
The use of edge computing provides a more detailed level of oversight and autonomy in industrial environments. On the other hand, Cloud applications offer centralized management and monitoring, enabling administrators to oversee multiple edge devices, applications, and data streams from a single interface. This centralized approach simplifies system configuration, updates, and maintenance, which ultimately reduces operational overhead and improves the overall reliability of the system.
Furthermore, the development of edge computing capabilities has played a significant role in the ease of managing industrial system. Edge computing brings the processing and analysis of data closer to its source, resulting in decreased latency and faster response times. This is particularly crucial in industrial settings where real-time decision-making is of utmost importance.
Therefore, Industrial Edge and Cloud architectures offers manufacturers the advantage of real-time insight into their production processes. This enables companies to engage in proactive maintenance, optimize quality, and allocate resources efficiently. These technologies also enable predictive analytics and maintenance and contribute to reducing downtime. As the connectivity of industrial devices expands, it becomes crucial for manufacturers to adhere to reliable protocols such as MQTT. This protocol can be seamlessly integrated with established IT security measures, making it the preferred choice for securing industrial applications. In addition, companies can utilize the Cloud for remote monitoring and control, enhancing the agility and flexibility of their production processes.


